Curriculum and Approach
Curriculum and Approach
Our school aligns our mathematics curricular approach with the broad aims of mathematics education in Singapore to enable students to:
-
acquire and apply mathematical concepts and skills;
-
develop cognitive and metacognitive skills through a mathematical approach to problem solving; and
-
develop positive attitudes towards mathematics.
Singapore Mathematics Framework
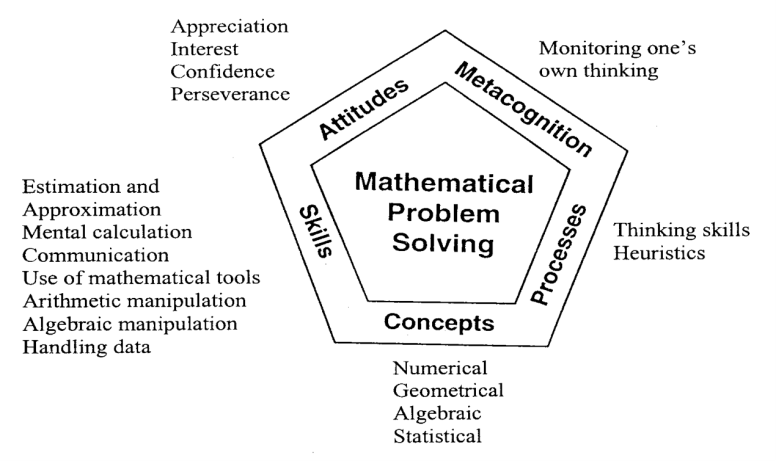
We achieve this by designing our math programme into 3 phases, with a focus on building strong foundation in the subject right from the start.
Si Ling Mathematics 6 year Programme
|
Phase |
Level |
Objectives |
|---|---|---|
|
PHASE 1: Laying the Foundation |
P1 and P2 |
Develop interest and enjoyment in learning mathematics.
|
|
PHASE 2: Building up the Skills and Processes |
P3 and P4 |
Build confidence in using mathematics. Develop reasoning, communication and problem solving skills. |
|
PHASE 3: Sharpening the Mathematical Skills and Processes |
P5 and P6 |
Apply reasoning, communication and problem solving skills.
|
Some of our common approaches:
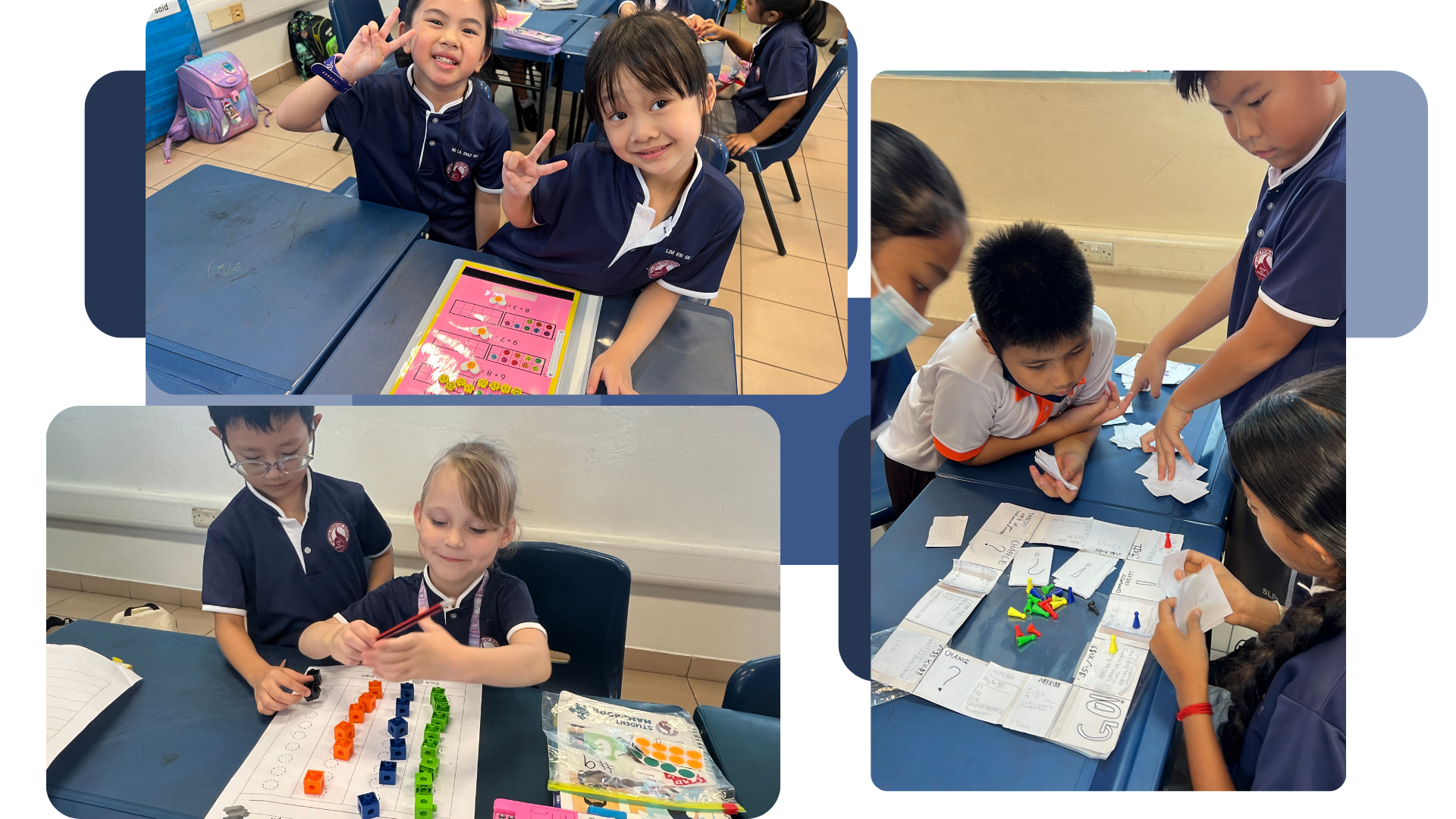
1. Concrete-Pictorial-Abstract (CPA) Approach
The Concrete-Pictorial-Abstract Approach (CPA) is used in the teaching of mathematics. Lessons are designed using the CPA sequence to foster deeper understanding of mathematical concepts.
Concrete is the “doing” stage. During this stage, students use concrete objects to model problems.
Pictorial is the “seeing” stage. Here, visual representations of concrete objects are used to model problems.
Abstract is the “symbolic” stage, where children use abstract symbols to model problems.

2. BEST Approach to Problem Solving
The Polya’s 4-step problem solving process was adapted and we called it the BEST approach to problem solving. This approach focus on metacognition which is thinking about thinking, refers to the awareness of, and the ability to control one’s thinking processes. This approach provides a structured development to pupils’ thinking process as they solve the word problem.
3. Model Method
The model method is used for effective mathematics learning and problem solving. The drawing of model helps our pupils understand complex mathematical word problems. It helps pupils to develop and enhance pupils’ mathematical thinking and problem solving in the early years of mathematical education.
4. Improving Confidence and Achievement in Numeracy (ICAN)
In Si Ling, we embarked on the ICAN programme by the Ministry of Education (Curriculum Planning and Development Division) to enhance the teaching and learning of mathematics. ICAN uses intervention strategies guided by research to address 4 key issues namely learning gaps, language, motivation and memory.
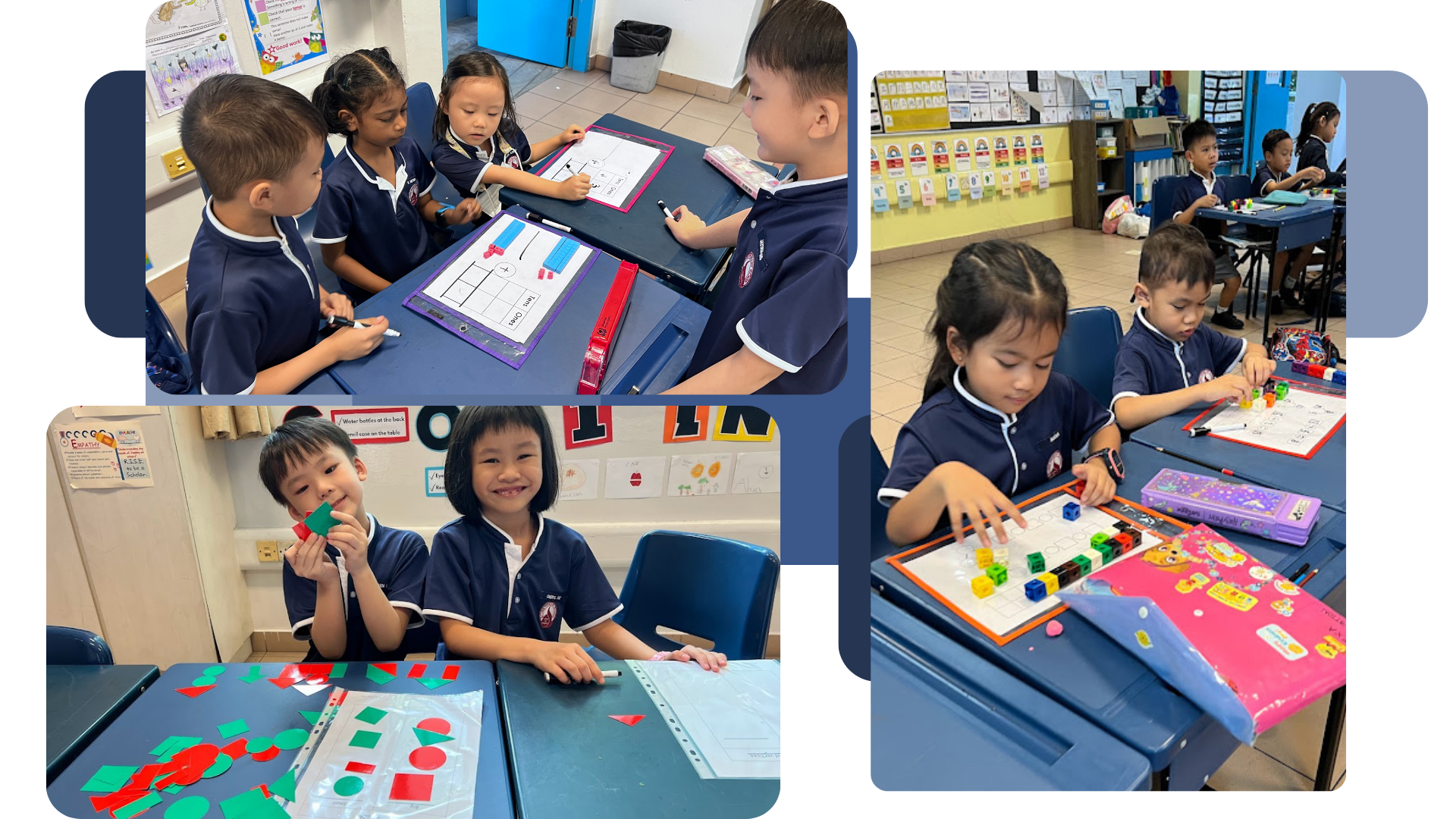

The ICAN principles
-
Routines and Norms
-
Diagnosis and Feedback
-
Practice and Review
-
Explicit and Direct Instructions
-
Scaffolding and Progression
-
Key Ideas and their Connections
-
Communication and Reasoning
-
Confidence and Motivation

